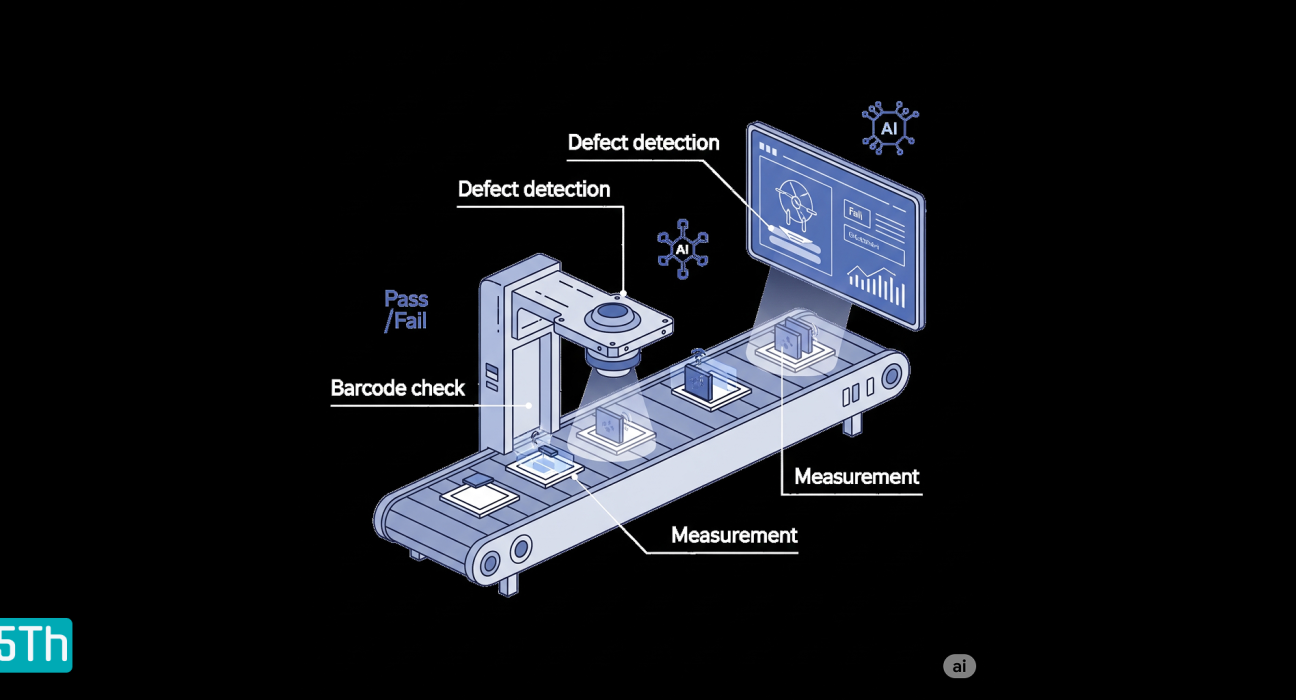
Quality control has always been a bottleneck in high-speed production environments. Human inspectors get tired, lighting conditions change, and defects slip through. That’s where machine vision steps in — combining cameras, sensors, and intelligent algorithms to spot flaws in real time with incredible precision.
📸 What Is Machine Vision?
Machine vision refers to the use of cameras, image processing software, and AI to “see” and interpret the visual aspects of a product, component, or environment.
Unlike human vision, machine vision:
- Is consistent (24/7 operation)
- Works at high speed (ms-level image processing)
- Can detect subtle anomalies that humans miss
It’s used across:
- Assembly lines
- Packaging systems
- Surface inspection
- Dimensional accuracy checks
- Barcode/QR code reading
🏭 Use Cases in Quality Control
🔹 1. Defect Detection in Manufacturing
Surface scratches, cracks, discoloration, missing parts — all can be automatically detected using machine vision, reducing the need for manual inspection.
Example: An aluminum extrusion plant in UAE uses high-speed line scan cameras to detect micro-defects in real time.
🔹 2. Label and Barcode Verification
Ensures labels are present, correctly printed, and properly aligned — especially critical in pharma, food & beverage, and retail.
Example: A packaging facility in KSA uses Cognex vision sensors to check pharmaceutical labels for accuracy.
🔹 3. Dimensional Measurement
Machine vision systems measure lengths, widths, angles, and even complex contours to ensure parts meet tight tolerances.
🔹 4. Assembly Verification
Checks whether all parts are present and correctly assembled — often integrated with robotic systems.
🔹 5. Color & Pattern Matching
Used in textiles, printing, and automotive industries where color consistency is crucial.
🤖 AI + Machine Vision = Smart QC
Modern machine vision systems are increasingly AI-powered:
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) classify defects with high accuracy
- Anomaly detection models identify “abnormal” but undefined flaws
- Edge AI devices process data locally with minimal latency
These tools not only detect issues but learn from patterns, making them ideal for continuous improvement in automated QC loops.
📉 Benefits of Machine Vision in QC
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Consistency | Eliminates variability from human error |
| Speed | Real-time inspection without slowing production |
| Cost Saving | Reduces rework, scrap, and recall risk |
| Compliance | Meets ISO and industry-specific QC standards |
| Traceability | Image logs for every inspected unit |
🌍 Adoption in the GCC
In the GCC, machine vision adoption is growing, particularly in:
- F&B (automated inspection of packaged goods)
- Pharma (anti-counterfeiting, serialization)
- Oil & Gas (pipeline inspection, flare monitoring)
- Automotive (weld inspection, part alignment)
Governments supporting smart industry programs (e.g., Vision 2030, In-Country Value programs) are driving adoption across national and private sector factories.
Pro tip: Look at COMEX Oman or GITEX UAE booths for emerging machine vision integrators and distributors.
⚠️ Challenges & Considerations
- Lighting conditions can affect camera accuracy
- Initial cost for camera systems, lenses, lighting, and software
- Integration complexity with existing PLC/MES/SCADA systems
- AI training data requirements if using custom models
Still, the ROI becomes clear after just a few months in medium to high-speed production lines.
✅ Conclusion
Machine vision is no longer a futuristic concept — it’s a current necessity for any business serious about zero-defect production and automated, scalable quality control.
Whether you’re inspecting engine parts, labels, or food packages, machine vision delivers measurable improvements in efficiency, reliability, and compliance.